Key Events in the History of Sustainability
In the present time, sustainability is defined as “meeting the needs of the present generation without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.” Sustainability has three main pillars: social, environmental, and economic. Any decision that creates a balance between these pillars can be considered sustainable. The history of sustainability can be seen in the century-old Egyptian civilisation, the 1700s agricultural revolution, and the 1970s and 1980s, which witnessed revolutionary sustainable development actions.
Table of Contents
ToggleToday, sustainability has become a critical global topic due to rising inequality, climate change, gender discrimination, wars, and rapid economic growth in developing and developed countries. Addressing and solving this issue requires a better understanding of sustainability. This article discusses the history and evolution of Sustainability.
Beginning of Sustainability in the Early Century
The agricultural, spiritual, and cultural traditions of early human communities revealed a deep knowledge of the environment and sustainability. This awareness comes from living experiences of harmony with the earth and its cycles rather than just an understanding of ecology as we know it today. Ancient civilisations, Indigenous people, and other early cultures created customs that demonstrated a profound comprehension of natural processes and the significance of preserving environmental equilibrium.
Ancient Civilisation Role in Sustainability

Ancient civilisation has much evidence of sustainability in the field of agriculture, ecology, water management, and environmental balance. Most of the evidence is visible in Mesopotamia, Ancient Egypt, and Ancient Greece. The following part shows how these civilisations adopted sustainability.
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia, a region in modern-day Iraq, was a pioneer in sustainable agriculture in the mid-period, relying on irrigation for crop survival. The Mesopotamians knew water’s importance and built extensive irrigation systems to support crops like barley and wheat. However, overuse led to soil salinization, impacting agricultural productivity. This highlights the ancient people’s limited understanding of environmental limits and the consequences of overexploiting natural resources.
Ancient Egypt:
Water management and agricultural practices were integral to Egyptian life, with the Nile River being a key source of water. The Egyptians utilized canals and reservoirs to control flooding, transforming the harsh desert into a sustainable agricultural zone. Their spiritual view of nature, influenced by gods like Ra and Osiris, emphasized the importance of nature for survival and religious life.
Ancient Greece
Greek philosophers like Aristotle and Theophrastus viewed nature as a well-ordered system, emphasizing the importance of balance in ecosystems. They documented plant species and their environmental needs, demonstrating the importance of balance in nature. The Greeks also practiced sustainability in agriculture, focusing on crop rotation, land stewardship, and soil fertility. Their understanding of ecology was often framed in terms of the “philosophy of nature,” emphasizing the significance of balance in nature.
Religious and Cultural Views on Nature and Sustainability
Religious and spiritual beliefs have significantly influenced the way different cultures view and interact with nature. Hinduism emphasizes the interconnection of all life and the importance of dharma (righteous living) in maintaining ecological balance. Sacred rivers and animals are revered, and the protection of water sources is seen as a religious duty. Buddhist teachings emphasize the importance of compassion for all beings, ahimsa (non-violence), and interdependence, as well as the need for sustainable living.
Christianity, on the other hand, emphasizes stewardship of creation, with many branches emphasizing the responsibility of humans to care for the Earth. The Book of Genesis presents humanity as stewards of God’s creation, tasked with cultivating and maintaining the natural world. While some interpretations of Christianity emphasize “dominion” over nature, others emphasize that dominion comes with responsibility. The Ecological Theology movement within Christianity advocates for environmental care as a moral and religious imperative, interpreting scriptures as urging humans to care for the Earth.
Sustainable practices in Christianity align with the teachings of compassion and care for God’s creation, leading to movements like Christian environmentalism. These religious and spiritual beliefs highlight the importance of preserving and preserving the environment for the well-being of all living beings.
The Industrial Revolution and its Impact on the Environment

The Industrial Revolution, which started in the late 18th century and continued into the 19th century, was a period of technological advancement, and social and economic change. As this advancement happened mass production and urbanization increased, because of this exploitation of natural resources, and the degradation of the environment increased at a rapid rate. The following part explores how the Industrial Revolution paved the way for the birth of environmental concern and the emergence of the conservation and sustainability movements.
Technological Advancements and Rapid Urbanization
Mass Production: The Industrial Revolution, characterized by mass production, led to an unprecedented increase in output in industries like textiles, iron, and coal. This led to a surge in demand for raw materials, causing the extraction of natural resources at an unsustainable rate. Forests were cleared for timber and agricultural expansion, while coal mining and iron smelting altered landscapes and ecosystems. The steam engine, which powered factories, trains, and ships, relied heavily on coal, a nonrenewable fossil fuel, releasing large amounts of pollutants into the air.
Rapid Urbanization effects: Urbanization and pollution also occurred due to the shift in population from rural areas to cities. The burning of coal for energy in factories and homes resulted in significant air pollution, smog, soot, and toxic gases. Water pollution was also a significant issue, with factories discharging untreated waste into rivers and streams, contaminating natural water systems. Deforestation and habitat loss were also significant consequences of the Industrial Revolution.
Early Signs of Environmental Concern and Conservation Movement

With the rapid environmental changes caused by industrialization, several thinkers, activists, naturalists, and environmentalists began to express concerns about the degradation of the environment and advocate for its Protection. These awnings paved the way for the foundation of the conservation and sustainability movement.
John Muir and the Birth of Conservation: John Muir, a Scottish-American naturalist and founder of the Sierra Club, advocated for nature and wilderness areas in the U.S., particularly in western states. He emphasized the intrinsic value of nature and the importance of preserving it for future generations. Muir’s philosophy of deep ecology, which included Yosemite National Park, influenced the conservation movement. The Sierra Club, founded by Muir in 1892, became an influential environmental organization, advocating for the protection of wilderness areas, national parks, and wildlife, balancing development with natural space preservation.
Ralph Waldo Emerson and Henry David Thoreau: Ralph Waldo Emerson and Henry David Thoreau significantly influenced early environmental thought, emphasizing the spiritual and moral importance of nature. Emerson’s philosophy emphasized the spiritual and moral teachings of nature, while Thoreau’s Walden Pond retreat criticized industrialization’s destructive effects on human life and the environment. Thoreau’s writings emphasized the disconnect between industrial society and nature.
Environmental Legislation and Early Policy
The National Parks Movement in the U.S. began in 1872 with the establishment of national parks like Yellowstone, marking the beginning of federal efforts to conserve wilderness areas.
The Antiquities Act of 1906, signed by President Theodore Roosevelt, granted the president the authority to preserve public lands as national monuments, protecting significant natural and cultural resources from exploitation.
The Birth of the Modern Sustainability Movement

The emergence of the modern sustainability movement begins with environmental awareness in the post-World War II era. Building concerns over industrialization’s environmental impacts, urbanization, and loss of resources led to a surge in efforts to address these issues. Several key events and figures, particularly in the mid-20th century, set the stage for what would later become a global environment movement.
Post-World War II Awareness
Post-WWII industrialization led to rapid growth in manufacturing, technology, and consumer goods, but also led to environmental degradation due to urban sprawl, pollution, resource depletion, and the widespread use of harmful chemicals. Rachel Carson’s Silent Spring, published in 1962, was a pivotal moment in the environmental movement, as she documented the harmful effects of pesticides, particularly DDT, on wildlife and human health, raising public concern about environmental pollution.
The Environmental Movement
Earth Day (1970) marked the birth of the modern environmental movement, with over 20 million people participating in rallies, educational events, and demonstrations. The event, initiated by U.S. Senator Gaylord Nelson, mobilized millions of people across the United States to demonstrate a cleaner, healthier environment. Key legislation introduced in the 1960s and 1970s, such as the Clean Air Act (1970) and Clean Water Act (1972), aimed to regulate air pollution and water pollution, respectively. On a global scale, international organization like the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), were established in 1972. These events solidified the environmental movement into a broad-based grassroots effort, attracting individuals from diverse backgrounds and political affiliations to support environmental protection.
Sustainability in the Late 20th Century

The concept of sustainable development began in the latter half of the 20th century. It is also a period in which sustainable development seeks to balance economic growth, environmental protection, and social equity.
Concept of Sustainable Development
The Brundtland Report, 1987: The Brundtland Report, published in 1987, revolutionized the global conversation on sustainable development. It defined sustainable development as meeting present needs without compromising future generations’ ability to meet their own needs. The report emphasized intergenerational equity, addressing environmental, economic, and social issues, laying the foundation for modern sustainability policies.
The Earth Summit and Kyoto Protocol: The 1992 Earth Summit in Rio de Janeiro was a pivotal event in the development of sustainable development policies. Key outcomes included the Agenda 21 framework and the Convention on Biological Diversity.
The Kyoto Protocol, adopted in 1997, aimed to reduce global greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change. Although its impact was limited, it served as a precursor to later agreements like the Paris Agreement, promoting sustainable development and biodiversity.
Sustainability in the 21st Century
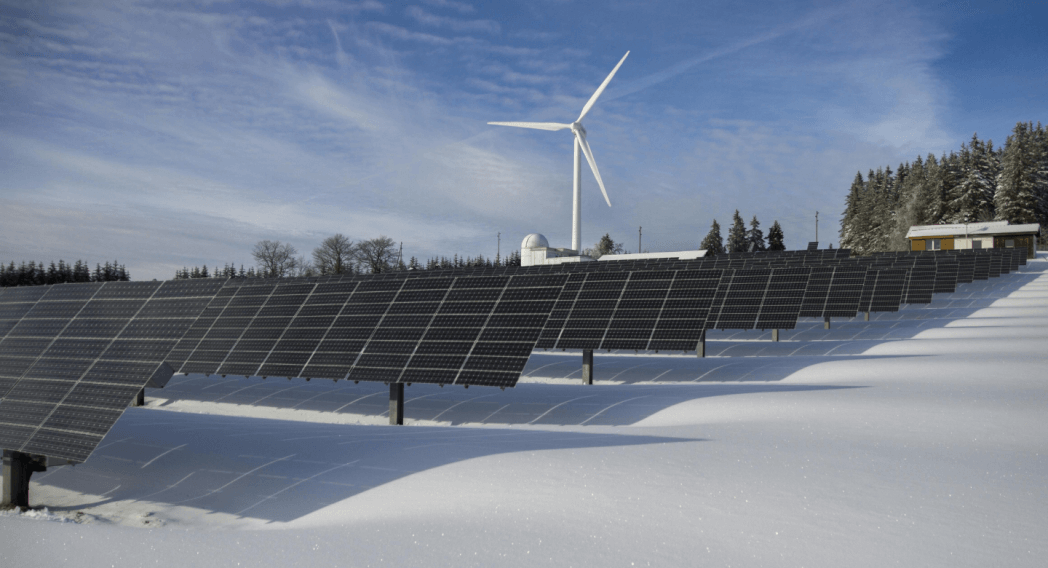

The 21st century has seen a rapid advancement in technologies and policies designed to address sustainability challenges worldwide. It’s also highlighting the urgent need for collective action to combat climate change and environmental degradation.
The Rise of Green Technologies
Renewable Energy: The research and development in solar, wind, hydropower, and geothermal energy have revolutionized the energy sector, by raising investments in renewable sources as alternatives to fossil fuels.
Electric Vehicles (EVs): The development of electric vehicles, led by companies like Tesla, tata, and others, has significantly impacted the automotive industry. Compared to traditional cars EVs produce fewer emissions and reduce the carbon footprint in the transportation sector.
Circular Economy: This model focuses on reducing waste and reusing materials through producing and designing products with sustainability in mind, recycling, repurposing, and reducing consumption.
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)

The United Nations introduced the Sustainable Development Goals SDGs) in 2015. It’s a global framework with 17 goals aimed at addressing key Challenges. These challenges include poverty, inequality, climate change, environmental degradation, and peace. SDGs aim to ensure prosperity for all while protecting the planet for the coming generation. It also provides a blueprint for governments, MNCs, NGOs, and individuals to work together to create a more sustainable and equitable world.
Modern Challenges and Solutions
Climate change is a pressing global issue causing rising temperatures, extreme weather events, and sea-level rise. To mitigate this, efforts include carbon pricing, reducing emissions, and transitioning to renewable energy sources. Biodiversity loss is accelerating due to habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change. Conservation efforts include establishing protected areas, restoring ecosystems, and enforcing anti-poaching laws. Addressing pollution, particularly plastic waste, air quality, and water contamination, is crucial. Innovations in waste management, recycling programs, and policies are essential for improving global environmental health. Grassroots movements, like Greta Thunberg and Extinction Rebellion, have raised awareness and pushed for urgent action. Technological innovation, policy changes, and global cooperation are essential for solving these complex environmental challenges.
Conclusion
The journey toward sustainability has been long; from early human practices that had environmental stewardship in them, to a worldwide movement that is now pressing for urgent action. The process of societies and people has shifted from natural resource exploitation to an increasing acknowledgment of the necessity to protect and conserve the planet Earth. From the ancient practice of agriculture to industrialization which led to the modern environmental movement, sustainability has evolved into an important aspect of our approach toward development, economics, and social progress.
In this respect, as we confront such critical challenges as climate change, biodiversity loss, and resource depletion, the evolution of sustainability is an ongoing process. Global cooperation, local action, and individual responsibility all come into play in the formation of a sustainable future. Every little effort counts to make the planet habitable for the generations to come.
Sustainability is no longer an option; it has become a necessity. Today’s collective actions will define whether humanity and the Earth survive and thrive. The time is now, and for that sustainable future, it’s time to take innovation, responsibility, and shared commitments to protect the environment as part of the journey.
References
History of SD · What is sustainable development · Sustainable Development Commission. (n.d.).
FutureLearn. (2022, October 25). Updates, Insights, and News from FutureLearn | Online Learning for You. FutureLearn.
Dhanani, R. (2024, August 17). A Brief History of Sustainability. The Sustainable Agency.
Steinbrink, L. (2024, October 29). The Evolution of Sustainability: A Journey of Environmental Awareness. Emerald built environment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on the History and Evolution of Sustainability
What is the history of sustainability?
Sustainability’s roots can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where early societies practiced sustainable agriculture and resource management. Over time, the industrial revolution led to environmental degradation, which sparked modern environmentalism in the 20th century, leading to global agreements like the Paris Agreement and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
When did sustainability become a global issue?
Sustainability became a global issue in the 20th century, particularly after the publication of Rachel Carson’s Silent Spring in 1962, which raised awareness about the dangers of pesticides. The formation of Earth Day in 1970 and the Stockholm Conference in 1972 marked significant global efforts to address environmental concerns.
How did the Industrial Revolution affect sustainability?
The Industrial Revolution led to mass production, urbanization, and exploitation of natural resources, causing severe environmental pollution and depletion. It was a turning point that highlighted the need for sustainability practices to balance economic growth with environmental protection
What was the Brundtland Report, and why is it important?
The Brundtland Report, published in 1987 by the UN’s World Commission on Environment and Development, introduced the concept of “sustainable development,” defining it as development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. It has since shaped modern sustainability frameworks.
How did Earth Day influence the sustainability movement?
The first Earth Day celebrated in 1970, mobilized millions of people around the world and raised awareness about environmental issues such as pollution, deforestation, and wildlife conservation. It marked the beginning of the modern environmental movement and spurred environmental laws and regulations.
What is the role of international agreements in sustainability?
International agreements, such as the 1992 Rio Earth Summit, the 1997 Kyoto Protocol, and the 2015 Paris Agreement, play a crucial role in setting global targets for climate action, pollution control, and conservation. These agreements facilitate cooperation between countries to address environmental challenges collectively.
What are the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)?
The SDGs are 17 global goals set by the United Nations in 2015 to end poverty, protect the planet, and ensure prosperity for all. These goals encompass areas like climate action, clean energy, responsible consumption, and biodiversity, aiming for a balanced and inclusive future for all.
How has corporate responsibility evolved in sustainability?
Corporate responsibility in sustainability has evolved from basic compliance with environmental laws to a more proactive role in promoting sustainability through green technologies, resource conservation, and social responsibility initiatives. Companies now report on their environmental impact and adopt practices like carbon-neutral operations and circular economies.
Why is the circular economy important for sustainability?
The circular economy aims to minimize waste and make the most of available resources by reusing, recycling, and upcycling products rather than following a linear model of production and disposal. It helps reduce environmental impact and promotes a more sustainable and efficient way of using resources.
What actions can individuals take to support sustainability?
Individuals can support sustainability by adopting eco-friendly habits such as reducing waste, conserving energy, choosing sustainable products, supporting environmentally responsible companies, and advocating for policies that protect the environment. Every small change counts in the collective effort to build a more sustainable future.







[…] Read More about the history and Evolution of Sustainability […]